Editorial - Journal of Contemporary Medical Education (2021)
Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Ana Margarida Mesquita*Ana Margarida Mesquita, Department of Pharmacology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Germany, Email: mesquita.amb@123.com
Received: 03-Dec-2021 Published: 24-Dec-2021
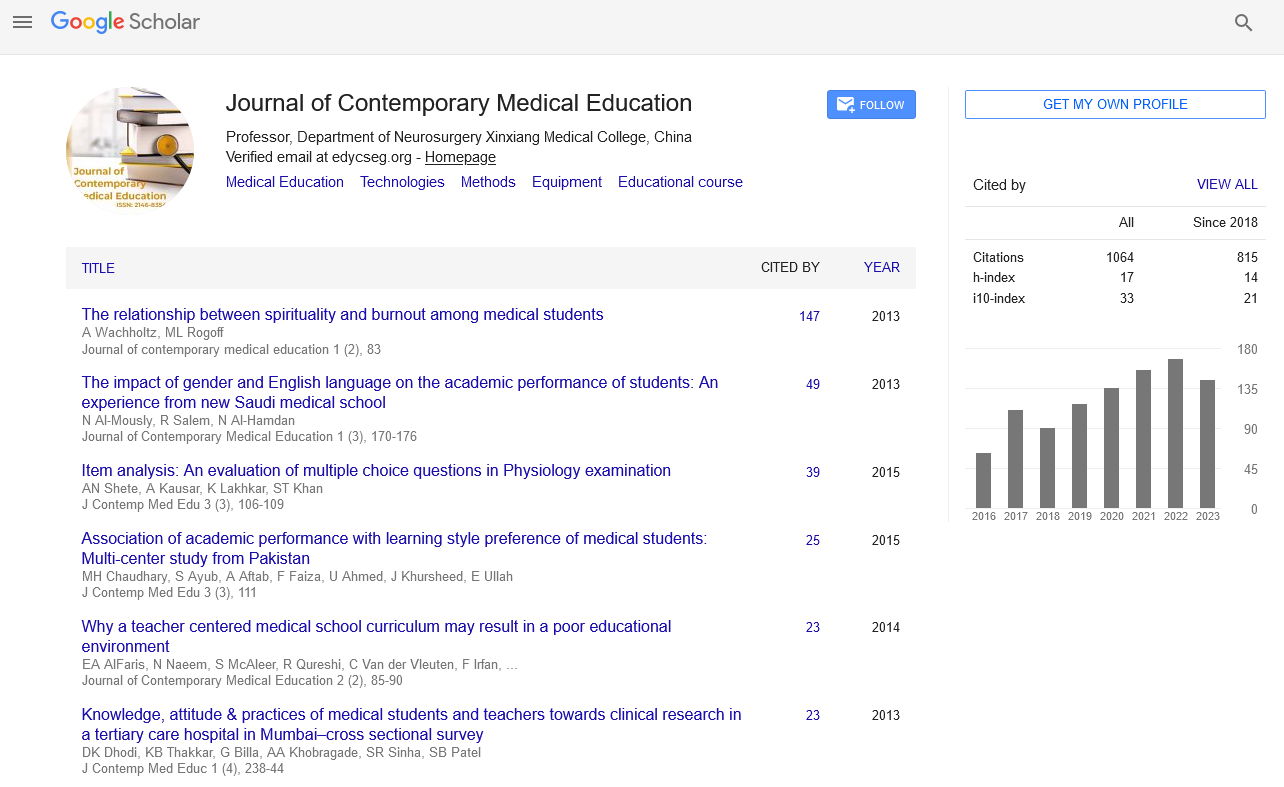
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is normal in ladies moderately aged and more established, and its clinical weight will increment as the populace ages. Notwithstanding hazard factors like age, equality, vaginal conveyance, and weight list (BMI), we examined the effect of schooling level on POP. Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) alludes to the prolapse of the pelvic organs brought about by unusual floor muscles and tissues and appears as strange organ position and organ brokenness. The principle manifestation is vaginal prolapse, which influences the patient’s personal satisfaction to fluctuating degrees. POPs are normal in moderately aged and more seasoned ladies. Global examinations have announced that pervasiveness of POPs goes from 2.9 to 41.1% [2-5]; commonness of indicative POPs in China is 9.6%. With expanded populace maturing, the predominance of POP will proceed to rise and the clinical weight will likewise increment. The gamble variables of POP are multi-layered. A deliberate survey in 2015 tracked down that age; equality, vaginal conveyance, and weight list (BMI) were altogether connected with the event of POP. Other conceivable gamble factors incorporate a background marked by macrosomia conveyance, careful birthing assistance, weighty actual work, persistent hack, clogging, and smoking. Social and financial variables may likewise unquestionably affect POP, and there are huge contrasts in the pervasiveness of POP among ladies with various financial levels. In this review, we gathered short term data of patients with “vaginal prolapse” as the principle protest in the gynecological center of the Third Hospital of Peking University from January 2017 to December 2020. We dissected the epidemiological attributes of patients with various financial levels to distinguish target populaces for POP counteraction and schooling. The incorporation rules were grown-up female patients with “vaginal prolapse” as the primary protest in the gynecological facility of our middle from January 2017 to December 2020. Every tolerant was reviewed by a doctor with experience in pelvic organ prolapse evaluation. Five patients with vaginal divider sores or in whom POP was absent during assessment were rejected. Patients with low schooling were more seasoned than patients with normal instruction or higher, and they had higher BMIs, more vaginal births, more gamble factors for POPs, and longer timeframes. The time from beginning to treatment is additionally longer. More consideration is required in this gathering of patients to forestall and treat POPs. The mean age of the patients was 63.4 ± 13.4 years and the mean BMI was 24.4 ± 3.1 kg/m2. Age, BMI, rate of birth, number of high gamble elements and years since illness beginning were altogether higher in bunch A than in different gatherings. BMI, equality and number of high gamble factors were essentially lower in bunch D than in different gatherings. There were no huge contrasts in the appropriation of patients in each gathering throughout recent years. Of the 993 included patients, ages went from 21 to 97 years, with a mean ± standard deviation of 63.4 ± 13.4 years and a mean of 65 years. The BMI esteem range was 16.2 to 40.0 kg/m2, with the mean being 24.4 ± 3.1 kg/m2 and the mean 24.0 kg/m2. Time from beginning of vaginal prolapse at first visit went from multi week to 50 years, with a mean of 45.1 ± 76.7 months and a mean of two years. Equality goes from 0 to 8, with a mean of 1.98 ± 1.14 and a middle of 2. Every understanding had 0 to 5 high-hazard factors (mean 1.51 ± 0.99 and middle 1). Of the relative multitude of members, 169 were premenopausal and 691 ladies revealed their period since menopause. The length of menopause went from 1 to 55 years, with a mean of 17.9 ± 9.70 years and a mean of 17.0 years. A sum of 308 ladies (31.0%) was hospitalized for careful treatment.
Acknowledgement
None
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts.