Evaluation of general health condition, stress and depression among first year medical students
Abstract
Wilma Delphine Silvia CR, Jayashree Shankar appa Seeri, Vasudeva Devanahalli Siddappa
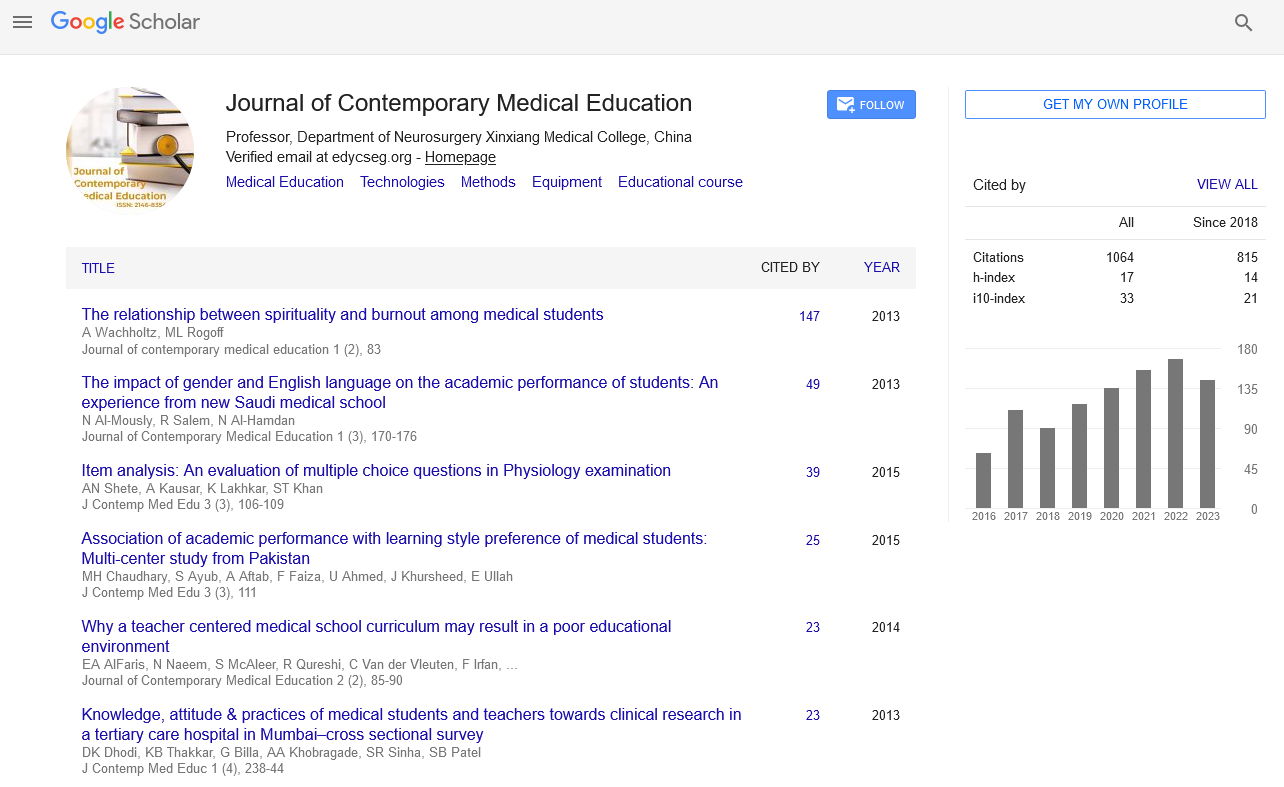
Stress appears to be universally prevalent entity in all students, regardless of their age sex, education, parent’s occupation, and presence or absence of a role model. Medical education is long and emotional taxing. Medical students thus experience tremendous stress during their undergraduate study. Hence the objective of this study was to evaluate general health condition and depression among first year MBBS students and also to determine the correlation between general health condition and depression. This study was a cross sectional and single centered study included 149 students of first year MBBS. In this study general health was assessed by using Goldberg’s general health questionnaire, depression was measured by Center for epidemiologic studies depression scale, student stress was measured by student stress survey questionnaire. Statistical analysis indicated the general health condition of students from urban background was significantly better than that of students from rural (P<0.05). The depression score among girls was significantly higher as compared to boys, 14.7% of the students were highly stressed and 79% had mild to moderate stress. Thus coping strategies can be adapted based on the quality and quantity of stress in medical students, which will help in preventing stress related disorders. Stress management increases motivation in students and better results in academic activities.
PDF